


 |  |  |
| | ||
Anaphylaxis
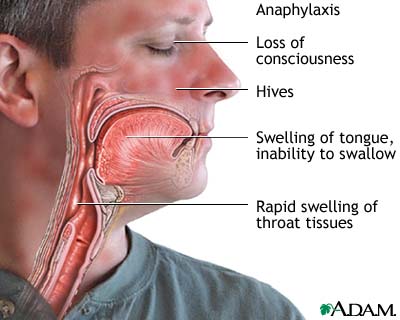
Anaphylaxis is an acute systemic (whole body) type of allergic reaction which occurs when a person has become sensitized to a certain substance or allergen and is again exposed to the allergen. Some drugs, such as those used for pain relief or for X-rays, may cause an anaphylactoid reaction on first exposure. Histamines and other substances released into the bloodstream cause blood vessels to dilate and tissues to swell. Anaphylaxis may be life-threatening if obstruction of the airway occurs, if blood pressure drops, or if heart arrhythmias occur.
Update Date: 10/12/2008 Updated by: Stuart I. Henochowicz, MD, FACP, Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine, Division of Allergy, Immunology, and Rheumatology, Georgetown University Medical School. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
