


 |  |  |
| | ||
Autosomal dominant genes
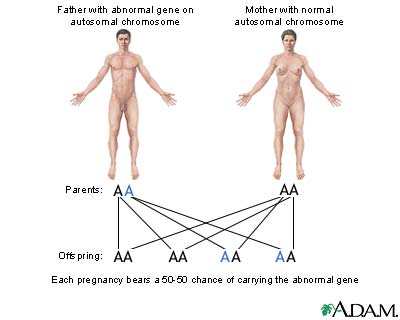
In the case of autosomal dominant genes, a single abnormal gene on one of the autosomal chromosomes (one of the first 22 "non-sex" chromosomes) from either parent can cause the disease. One of the parents will have the disease (since it is dominant) in this mode of inheritance and that person is called the CARRIER. Only one parent must be a carrier in order for the child to inherit the disease.
Update Date: 5/20/2008 Updated by: Diana Chambers, MS, EdD, Certified Genetics Counselor (ABMG), Charter Member of the American Board of Genetic Counseling, University of Tennessee, Memphis, TN. Review provided by VeriMed HealthcareNetwork. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.
