Area
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the physical quantity. For other uses, see Area (disambiguation).
Area is a physical quantity expressing the size of a part of a surface. The term can also be used in a non-mathematical context to be mean "vicinity".
Surface area is the summation of the areas of the exposed sides of an object.
Contents
|
[edit] Units
Units for measuring surface area include:
- square metre = SI derived unit
- are = 100 square metres
- hectare = 10,000 square metres
- square kilometre = 1,000,000 square metres
- square megametre = 1012 square metres
- square yard = 9 square feet = 0.83612736 square metres
- square perch = 30.25 square yards = 25.2928526 square metres
- acre = 160 square perches or 43,560 square feet = 4046.8564224 square metres
- square mile = 640 acres = 2.5899881103 square kilometres
[edit] Useful formulae
| Shape | Equation | Variables |
|---|---|---|
| Square |  | s is the length of the side of the square. |
| Regular hexagon |  | s is the length of one side of the hexagon. |
| Regular octagon |  | s is the length of one side of the octagon. |
| Perfect Hexagon |  | w is the width of one side when all sides are equal. |
| Perfect Octagon |  | w is the width of one side when all sides are equal. |
| Any regular polygon |  | a is the apothem, or the radius of an inscribed circle in the polygon, and p is the perimeter of the polygon. |
| Any regular polygon |  | P is the Perimeter and n is the number of sides. |
| Any regular polygon |  | P is the Perimeter and n is the number of sides. |
| Rectangle |  | l and w are the lengths of the rectangle's sides (length and width). |
| Parallelogram (in general) |  | b and h are the length of the base and the length of the perpendicular height, respectively. |
| Rhombus |  | a and b are the lengths of the two diagonals of the rhombus. |
| Triangle |  | b and h are the base and altitude (height), respectively. |
| Disk* or Circle |  | r is the radius. |
| Circle, Circular area |  , or , or  | r is the radius and d the diameter. |
| Ellipse | 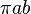 | a and b are the semi-major and semi-minor axes, respectively. |
| Trapezoid |  | a and b are the parallel sides and h the distance (height) between the parallels. |
| Total surface area of a Cylinder | 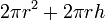 | r and h are the radius and height, respectively. |
| Lateral surface area of a cylinder |  | r and h are the radius and height, respectively. |
| Total surface area of a Cone | 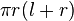 | r and l are the radius and slant height, respectively. |
| Lateral surface area of a cone |  | r and l are the radius and slant height, respectively. |
| Total surface area of a Sphere |  or or  | r and d are the radius and diameter, respectively. |
| Total surface area of an ellipsoid | See the article. | |
| Circular sector |  | r and θ are the radius and angle (in radians), respectively. |
| Square to circular area conversion |  | A is the area of the square in square units. |
| Circular to square area conversion |  | C is the area of the circle in circular units. |
* A disk is the area enclosed in a circle. Often such area is called cross-sectional or circular area like a round cable cut in half.